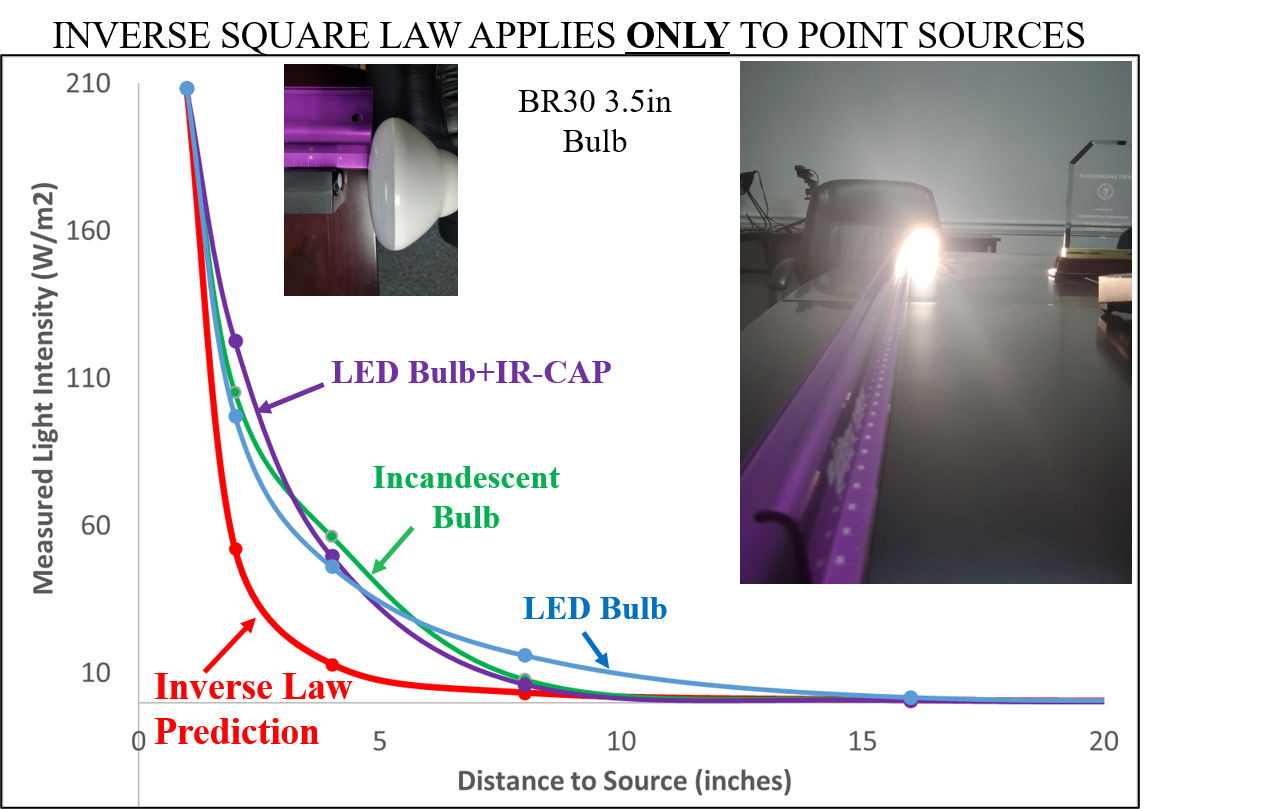
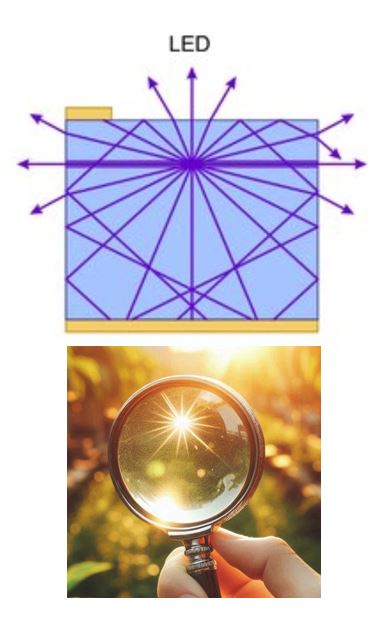
Fundamentally, an LED is an isotropic point source of light. However, light bulbs and fixtures are generally never exact point sources, unless we move significantly far away from them. The irradiance data below was taken using 3 different BR30 bulbs:
1. 2700K Incandescent Bulb (3.5in BR30 with reflector)
2. 2700K LED Bulb (3.5in BR30 with reflector)
3. 2700K LED Bulb + IR-CAP (3.5in BR30 with reflector)
The reflectors used in all the BR30s manipulate the light to be more directional, in order to illuminate over longer distances. This is true, even for the traditional incandescent. LED bulb and fixture designs are generally (but not always) more directional, so higher irradiance levels can be detected further away when compared to what we experience with incandescent bulbs. Couple that to the fact that standard LEDs emit significantly more blue and green-yellow light, which can overwhelm the eye’s photo-receptors.
Notice how the LED bulb with the built-in IR-CAP behaves more like an incandescent and less like a standard LED bulb. That’s because the IR-CAP provides an additional medium where LED light can be converted and scattered more isotropically.