Flexible & Printed Electronics, Photonics, and Organic LEDs
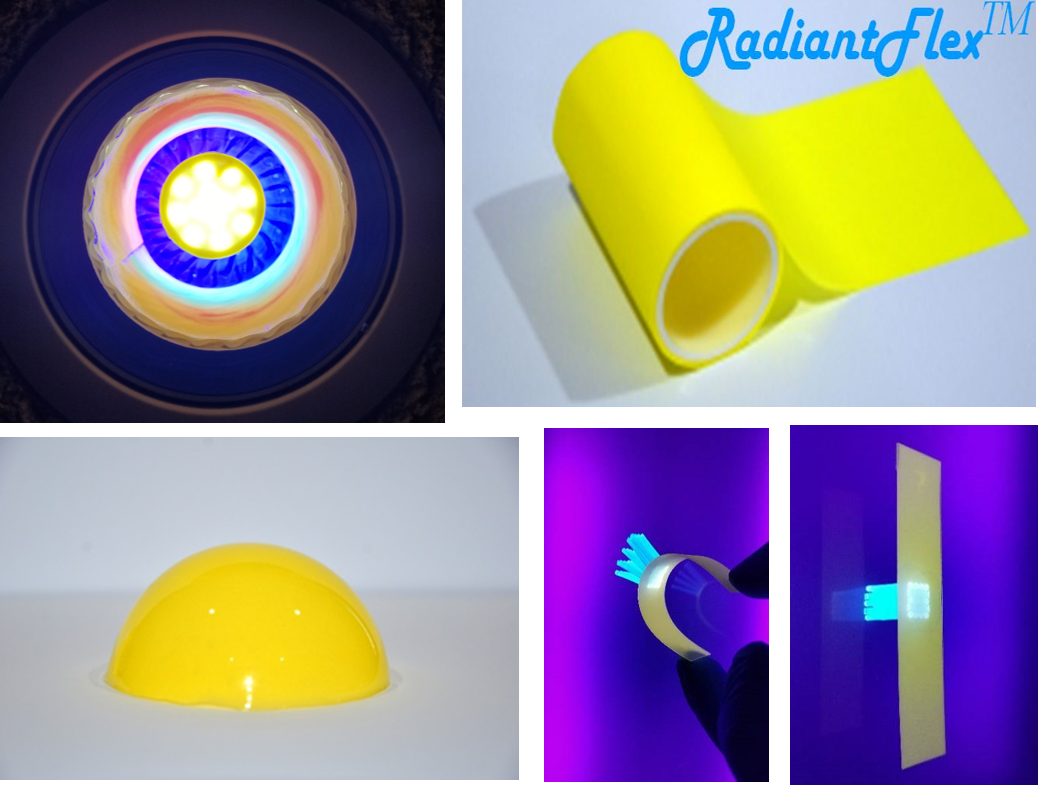
Flexible photonics/electronics is an evolving technology used for mounting or printing optical and electrical devices on various plastic substrates such as polyester, polycarbonate, polyimide, and even conductive (ITO or PEDOT) plastic films. Flexible phosphor films can be made on any type of flexible or rigid substrates including PET, PC, acrylic, styrene, aluminum, even flexible glass. Flexible phosphor films can help provide enhanced performance and capabilities for a wide range of applications including lighting, displays, photovoltaic, sensing, energy storage, batteries, automotive, horticulture, etc.
Flexible phosphor sheets can be printed on using a wide range of techniques such as screen printing, inkjet, and even 3D printing. Sheets can be made as thin as 150 microns or as thick as several millimeters. The sheets can be die-cut into a wide range of shapes and sizes to fit a particular light engine or optoelectronic device. All types of electronic devices and sensor components can be integrated with any phosphor in order to enhance the performance of scintillators, solar cells, solid-state lighting, and optical sensors across the electromagnetic spectrum.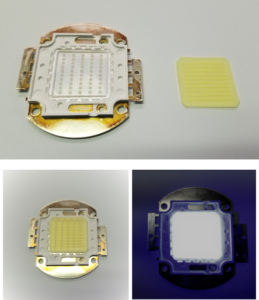
Phosphor films can also be made into 3-dimensional shapes using available plastic forming techniques such as vacuum forming or thermoforming. Thermoforming is a commonly used manufacturing process that involves heating plastic sheets and forming them using a mold to specific shapes. The shaped plastic is then cooled down and trimmed to the desired finished part. The process generally uses a thermoforming machine to heat up and stretch the thermoplastic sheet over the mold. Modern thermoforming machines generally have built-in capabilities to handle the trimming and cutting process, but for traditional systems trimming is generally conducted as a separate step. A wide range of thermo-formable plastic sheets can be used as substrate materials for phosphors and flexible photonics and they can be transparent, reflective, or diffuse, depending on the application.

