The term blue-pump phosphor refers to a phosphor that converts blue light from an LED into another light color, including white light. White light is basically light than contains all the colors of the visible spectrum. Phosphors that respond to blue light can be mixed together in order to deliver a broad white light spectrum covering the entire visible range.
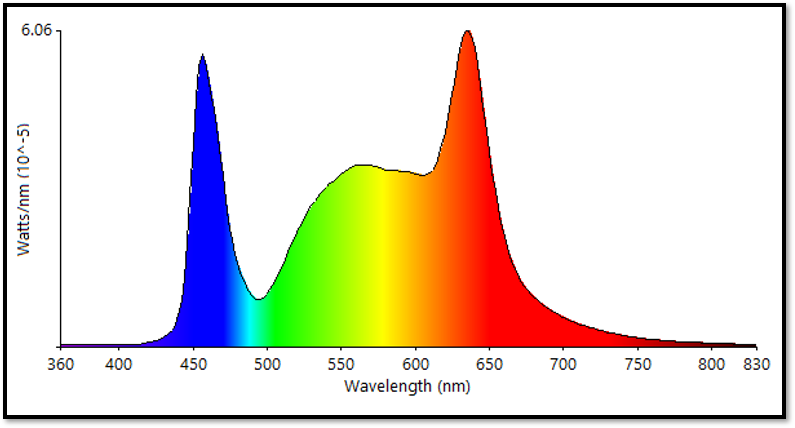
How a blue-pump phosphor works:
- A blue LED acts as a “pump” to excite the phosphor.
- The phosphor absorbs the blue light and converts it into other colors, like green, yellow, and/or red.
- If a phosphor mix produces all the colors, the resulting light will be white when mixed with the blue light from the LED.
Applications:
- White LEDs: Blue-pump phosphors are used in white LEDs for indoor/outdoor lighting, smartphones, laptops, TVs, etc.
- Infrared LEDs: Blue-pump phosphors can be used to create infrared light sources for spectroscopy applications in agriculture, healthcare, and retail. Infrared phosphors can also be incorporated in standard LEDs to create a more balanced light spectrum with focus on health and wellness.
- Laser lighting systems: Blue-pump phosphors can be used in laser lighting systems.
- Architectural lighting: Blue-pump phosphors can be used in architectural lighting.
- Vehicle headlights: Blue-pump phosphors are used in LED or laser-based vehicle headlights.
- Outdoor lighting displays: Blue-pump phosphors can be used in outdoor lighting displays.
Factors to consider:
- Phosphor layer thickness: The thickness of the phosphor layer affects the color characteristics of the color-converted LED.
- Thermal stability: Some phosphors exhibit high thermal stability, meaning they retain their emission intensity even at higher temperatures.
- Chemical stability: Some phosphors exhibit good chemical stability in ambient atmospheres and are more effective at resisting long-term degradation from moisture and heat.
- Cost: Some phosphors are made using more exotic elements and can be significantly higher cost to manufacture compared to others.
